I see. Makes sense.
Avid Amoeba
- 4 Posts
- 109 Comments

 115·4 days ago
115·4 days agoThis is the right way to optimize performance. Write everything in a decent higher level language, to achieve good maintainability. Then profile for hotspots, separate them in well defined modules and optimize the shit out of them, even if it takes assembly inlining. The ugly stays its own box and you don’t spend time optimizing stuff that doesn’t need optimization.

 8·14 days ago
8·14 days agoNot noticeable with always-on Tailscale with the default split-tunnel mode. That is when Tailscale is only used to access Tailscale machines and everything else is routed via the default route.

 3·15 days ago
3·15 days agoGoogle’s fine. They’re using ARM cores that are built on Samsung’s shittier manufacturing process. Next year they’re going TSMC which should improve power consumption dramatically. The lauded Dimensity 4000 also uses ARM cores, just newer and built on TSMC’s process. By the same token, newer Google SoCs should experience similar performance as they update the cores and manufacturing.

 51·15 days ago
51·15 days agoThe parent asked how do you define at all. What I wrote is just the dumbest way which demonstrates how it can be done. This dumb solution holds up even in your scenario because new media doesn’t gain significant user base every other year. If the list is outdated, containing Facebook and Instagram alone, that would still capture a huge part of the problem already. You can probably figure a slightly less dumb alternative that wouldn’t require amendments just to add another platform. Folks talking about the impossibility of defining something or implementing something in law often ignore obvious solutions, existing working processes, and present this false dichotomy of a perfect solution vs impossible to solve. Sometimes it’s a matter of ignorance, other times it’s driven by (conscious or subconscious) libertarian beliefs.

 91·15 days ago
91·15 days agoHere’s one way to do it. The legislators define a list. Products in the list are social media. The list is referenced in the law.

 401·16 days ago
401·16 days agoAlternative Title: “Bluesky happy to use the standard playbook so long as there’s still bozos willing to contribute free labor for their profit.”
TFTFY

 1·16 days ago
1·16 days agoThat’s funny but I’m not gonna argue on it. It’s easier to give another example. If you want to get informed try finding laws that depend on firm size and be convinced if you do.

 2·17 days ago
2·17 days agoWrong as in not sound. An argument can be valid assuming its assumptions are true. The argument is the model, which really is a set of arguments. Its assumptions which are taken axiomatically are as you say impossible, therefore they are not true (which I called wrong). So the argument is not sound. I’m not saying anything different than what you said really, just used informal language. ☺️

 15·17 days ago
15·17 days agoFor a firm that already have their own core designs that simply use the ARM instruction set, it might be easier to adapt to RISC-V. For a firm that licenses ARM cores on the other hand…

 21·17 days ago
21·17 days agoAre you telling me that the axioms behind the simplistic model are wrong??
shocked-pikachu.jpg
How do Signal stop forks from connecting to their servers?
The VPN should keep access to the homelab even when the external IP changes. Assuming the VPN connects from the homelab to the cloud. The reverse proxy would use the VPN local IPs to connect to services.

 5·24 days ago
5·24 days agoThe last time I activated a TV was in 2022. It was a Sony X85K and it didn’t require a connection. I’ve subsequently only used it with a CCwGTV.
Before that I activated a Samsung U…7300 or something like that in 2020. That didn’t require connection either. I also used it with a CCwGTV.

 491·24 days ago
491·24 days agoARM isn’t the x86 solution people like it to be. It’s at least as proprietary as x86 and the fact that it’s more widely licenced today than x86 is a happy coincidence. ARM licensing can dry up with a change in corporate leadership or a takeover by one of a myriad large corporations. A solution worth cheering would be a good enough open RISC-V core.

 3·24 days ago
3·24 days agoIf you’re switching low power inconsequential things like LED lights, they’re OK.

 9·24 days ago
9·24 days agoThis like most plugs in this format is not for inductive loads so it can only handle 300W with such:
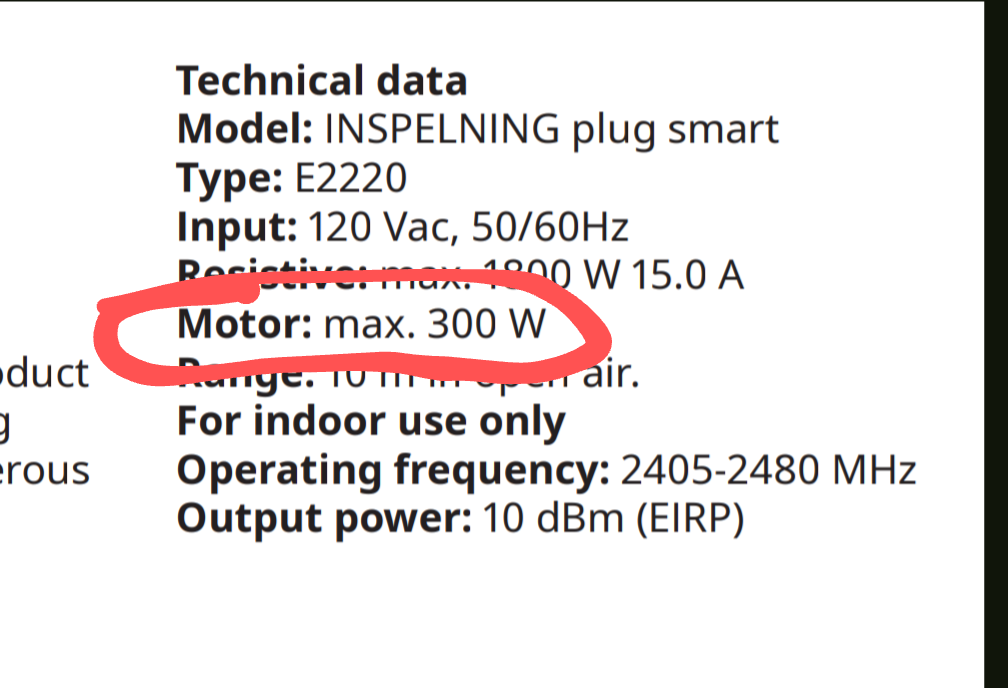
It might be OK if the AC units are small enough.

I find the intermediary classification a bit unconvincing and perhaps unintentionally misleading. It sounds like a nice framework to look at the world and it does describe the particular domain alright and it allows for drawing useful conclusions. Unfortunately solving the problems it highlights would produce marginal gains because I think intermediaries as described are just a special case of something more general. Firms of any kind are acting as intermediaries in the exchange of the products of people’s labor. The effects are all the same, these intermediaries make the exchange easier at the expense of keeping some of the labor products from one end or the other, but usually both. It seems to me that the problem of the platform intermediaries power is just a special case of the power of firms over labor. Which really reduces to the problem of the power of capital over labor. If we somehow solve the platform intermediaries problem, we leave the general problem unsolved. And then if we don’t think in terms of the general problem, we can’t even solve the special problem because the tools needed are controlled by capital. That is the lawmakers who could change the law are paid by the powerful intermediaries (firms) and not by the people on either end of the intermediaries. If we hope to ever solve any of this I think we have to look at the world through the general lens and focus on ways to reduce the amount of capital accumulated by firms from people’s labor. Fortunately there are well known solutions for that and they’re actionable for most people.